Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning otherwise known as UDL is defined as a framework that is used to improve and optimize learning and teaching for all learners based on scientific evidence on how humans learn. It aids in differentiation so that all learners can benefit. The framework reduces barriers to learning. Most educators use free, or low cost technology in order to implement this framework. This blog is dedicated to educational technology tools. Every single technology tool that can be used for instruction can be incorporated into this framework. The framework is based on three basic principles and nine guidelines. Below is an infographic that breaks down Universal Design for Learning.
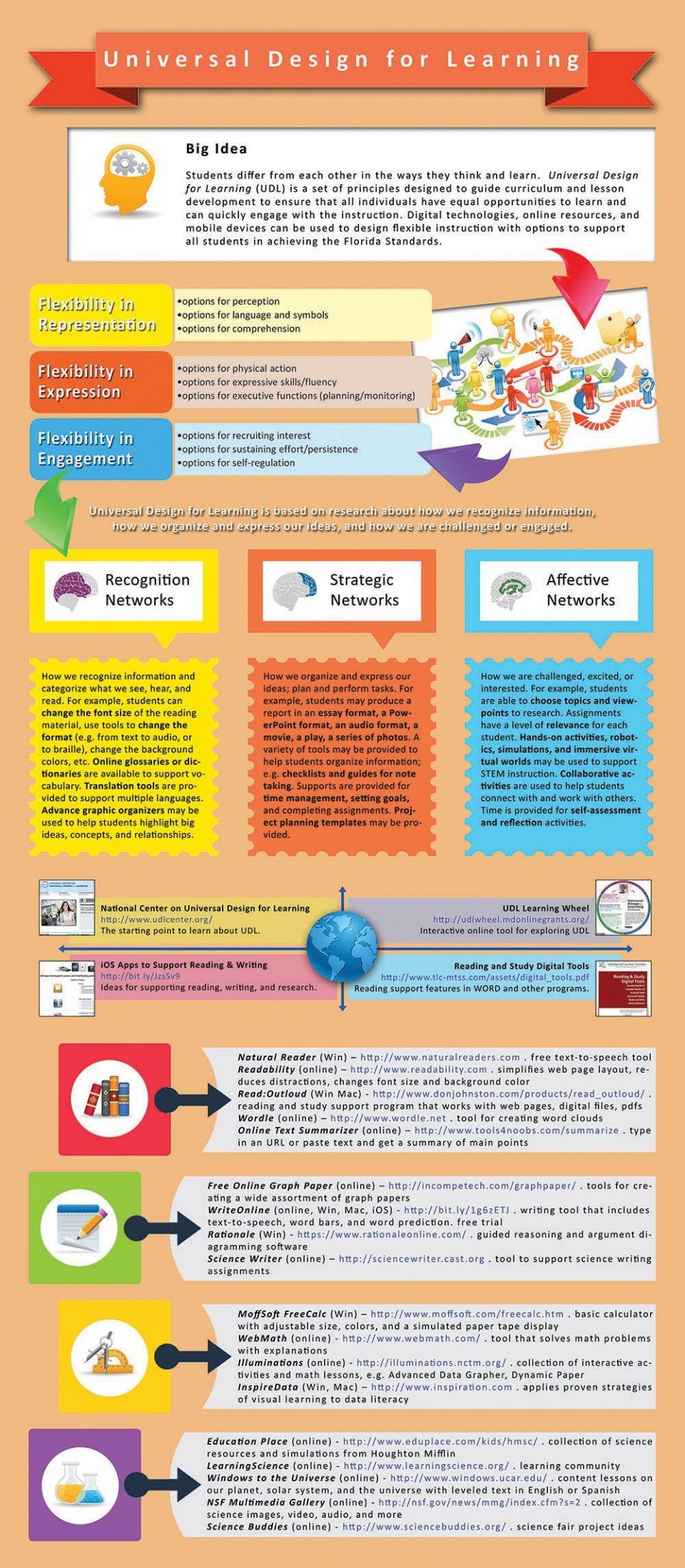


This infographic presents the basic principles of Universal Design for Learning (UDL), along with a variety of online resources to assist educators in implementing UDL in the classroom.
Here is an infographic of the UDL Guidelines:
Throughout my 11 year career as an educator, I have spent time studying and developing lessons using UDL. I was trained to incorporate all of the guidelines into my lessons so I use them all. Since I use them all, I think the guidelines that I could add more of to my teaching practice or those under the principle of engagement. Providing options for recruiting interest, sustaining effort and persistence, and self regulation are the guidelines that I have trouble with in terms of finding variety. I generally use the same activities and techniques over and over. I need to learn new techniques to switch it up in this area. Sustaining effort and persistence is the main guideline that I need some assistance with.
Since engagement is the principle of UDL that I need to improve upon, I decided to research how technology can help with this. There are so many different tools that can be used to engage. Audio books and Ebooks could be used instead of printed text, videos, google forms, google docs, social media such as twitter, Docent EDU, and Kaizena just to name a few.
References
Csillag, J. (2016, July 12). How to Use Technology to Support the UDL Principles in Reading. Corwin Connect. https://corwin-connect.com/2016/07/use-technology-support-udl-principles-reading/
Hall, T. E., Meyer, A., & Rose, D. H. (2012). Universal design for learning in the classroom: Practical applications. New York: Guilford Press.
UDL: The UDL Guidelines. (n.d.). Retrieved July 25, 2020, from http://udlguidelines.cast.org/
Universal Design for Learning (Part 1): Definition and Explanation. (2017, July 24). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hwPuJ4l_ukE&feature=youtu.be
Universal Design for Learning (Part 2): UDL Guidelines. (2017, July 24). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PNaafVoi2Ic
Universal Design for Learning (Part 3): Engagement Strategies. (2017, July 24).
Universal Design for Learning (Part 4): Representation Strategies. (2017, July 24). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9TVKGvnGPoA
Universal Design for Learning (Part 5): Action and Expression Strategies. (2017, July 24). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H66jHEiGNLQUniversal Design for Learning: UDL. (2019, December 18). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gmGgplQkrVw&feature=youtu.be


Wow, did you create that infographic for UDL? That's amazing. I like what you acknowledged that despite your 11 years working with UDL, you still have room for improvement. I believe there are a lot of teachers out there that have been doing the same thing because it's what they've always done.
ReplyDeleteThe infographic you shared was very easy to follow! This is great to share with other educators who are not aware of UDL. We all implement some of these guidelines, but seeing them as part of UDL reassures me that they are best practice.
ReplyDelete